Forschung
[TheCore] Enterprise Computing for Enterprise Systems
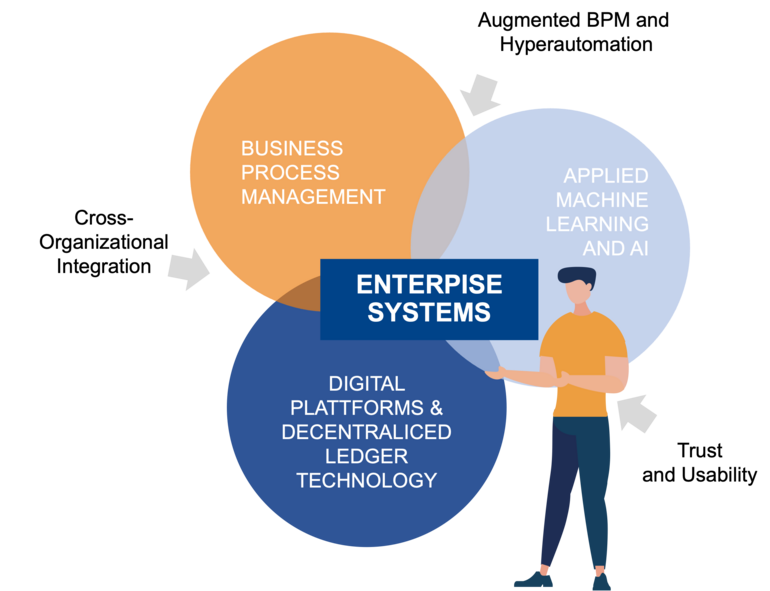
Our research primarily focuses on the field of business information systems. Within our chairs' broad scope, we explore a wide range of topics under the umbrella of "Enterprise Computing for Enterprise Systems." This includes, but is not limited to, process and data modeling, augmented Business Process Management (BPM), hyperautomation, the application of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning, as well as distributed computing and digital platforms.
Methodologically, our approach is anchored in design science research, encompassing both modeling and prototyping, alongside empirical and mathematical-formal research methods. To address pertinent research topics, we enhance our approach by integrating both empirical and quantitative methods. A significant aspect of our work is the development and evaluation of innovative methods and prototypes, which we actively apply and integrate into real-world contexts.
BPM with Augmented BPM and Hyperautomation
Applied ML and AI
Digital Platforms and Value Networks
Collaboration in value creation networks or supply networks serves to connect companies, which is playing an increasingly important role. Trends such as the sharing economy are currently changing established industries such as hospitality and transport. Digital platforms also represent an essential infrastructure and define the framework conditions for the interaction and relationship of the actors. In the B2B sector, this is increasingly giving rise to new platform-based business models that are highly relevant for the success of interorganisational cooperation. However, digital platforms not only create advantages, but also bring well-known problems such as information asymmetry and other complex decision-making processes of behaviourism back into focus.